average sample size for quantitative research|100 respondents for quantitative research : exporter exporters exporting Sample size is a critical determinant for Linear, Passing Bablok, and Deming regression studies that are predominantly being used in method comparison studies. Sample size estimations for . web21 de fev. de 2024 · The new user promotions below feature sportsbooks that have free bet offers, bet $ to win $ offers, and other first-bet bonuses! BetMGM Sportsbook Promo Code : GAMBLEUSA – $1000 Bonus Bet. bet365 Sportsbook Promo Code: N/A – $200 in Free Bets for $1 Bet. Borgata Promo Code : GUSA – Bet $20 get $100 Free Bet. Tipico .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Coroa Rabuda RebolandoAcesse: http://saibaagora.club/curadaejprecoceFaça acontecer na sua vida como .
Most statisticians agree that the minimum sample size to get any kind of meaningful result is 100. If your population is less than 100 then you really need to survey all of them. A good maximum sample size is usually 10% as long as . Determining an appropriate sample size is vital in drawing realistic conclusions from research findings. Although there are several widely adopted rules of thumb to calculate sample size,. You need to determine how big of a sample size you need so that you can be sure the quantitative data you get from a survey is reflective of your target population as a whole - and so that the decisions you make based on .Sample size is a critical determinant for Linear, Passing Bablok, and Deming regression studies that are predominantly being used in method comparison studies. Sample size estimations for .
A recent article suggests six ways to evaluate a sample size and its ability to provide noteworthy data, with added discussion on factors like resource limitations and the .A study that requires one to describe or compare detailed subpopulations generally requires a larger sample size than a study that requires one only to describe population parameters. .As a result, we outline the steps required to calculate sample sizes for probability-based surveys and then extend our discussion to calculating sample sizes for non-probability surveys (i.e., controlled samples) and experiments. .By Jim Frost 4 Comments. What is Sample Size? Sample size is the number of observations or data points collected in a study. It is a crucial element in any statistical analysis because it is the foundation for drawing inferences and .
In this article, we'll answer these questions about sample size in quantitative research: Why does sample size matter? How do I determine sample size? Which sampling .How to determine the correct sample size for a survey. Jump to main content. Search. Search. Close. Resource Type: Science Projects; . (which means that there is only a 5% chance of your sample results differing from the true population average), . Creative Research Systems, 2003. "Sample Size Calculator," Retrieved June 28, 2006 from https Sample size in quantitative instrument validation studies: A systematic review of articles published in Scopus, 2021 . additional research is needed to verify sample sizes in correlational studies. Second, these suggested sample size values are based on outlier-removed averages from articles published in quartile 1 and 2 journals, given that . Approaches to sample size calculation according to study design are presented with examples in health research. For sample size estimation, researchers need to (1) provide information regarding the statistical analysis to be applied, (2) determine acceptable precision levels, (3) decide on study power, (4) specify the confidence level, and (5 .
sampling formula for quantitative research
One of the major issues in planning a research is the decision as to how a sample and the method to be employed to select the estimated sample in order to meet the objective of the research.
A target sample size of at least 10 completed interviews was planned based on the likelihood of saturation and given our research goals and sampling strategy [33]. Rapid qualitative methods were .The reason why sample size calculators for experiments are hard to find is simple: experiments are complex and sample size calculations depend on several factors. The guidance we offer here is to help researchers calculate sample size for some of the simplest and most common experimental designs: t -tests, A/B tests, and chi square tests.
What is Sample Size? Sample size is the number of observations or data points collected in a study. It is a crucial element in any statistical analysis because it is the foundation for drawing inferences and conclusions about a larger population.. When delving into the world of statistics, the phrase “sample size” often pops up, carrying with it the weight of your study’s credibility . Sample size is a term used in market research to define the number of subjects included in a survey, study, or experiment. In surveys with large populations, sample size is incredibly important. The reason for this is because it's unrealistic to get answers or results from everyone - instead, you can take a random sample of individuals that . average sample size of approx. 50. . setting it apart from the more structured methodology of quantitative research. Contrary to sampling methods in quantitative research, which primarily aim to . Furthermore, our results show what a ‘small’ sample actually is, by providing a range of sample sizes for saturation in different qualitative methods (e.g., 9–17 interviews or 4–8 focus groups). This is important because general advice on sample sizes for qualitative research usually suggest higher sample sizes than this.
sample size in research methodology
Gale Academic OneFile includes Sample size in quantitative research: Sample size will by Susan B. Fowler and Valerie Lapp. Click to explore.
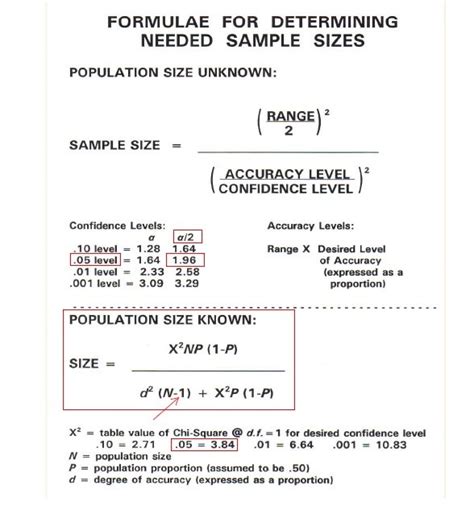
Here, the sample average originates from a Normal distribution with a mean of . Qualitative research approaches sample size determination with a distinctive methodology that diverges from quantitative methods. Rather than relying on predetermined formulas or statistical calculations, it involves a subjective and iterative judgment throughout .The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math skills. Cochran’s formula is perhaps the most well known equation for calculating sample size, and widely used when the population is large or unknown.
shimadzu universal testing machine uh-a-c series
That’s why we have built our DIY quantitative research sample size calculator. From some basic information, this tool displays the recommended sample size required for your research to be statistically significant. . Therefore a confidence level of N% means you can be N% sure that your results contain the true mean average of the designated . Sample adequacy in qualitative inquiry pertains to the appropriateness of the sample composition and size.It is an important consideration in evaluations of the quality and trustworthiness of much .
Efficiency: Quantitative research can be conducted relatively quickly and efficiently, especially when compared to qualitative research, which may involve lengthy data collection and analysis. Large sample sizes: .This free sample size calculator determines the sample size required to meet a given set of constraints. Also, learn more about population standard deviation. The Relationship Between Sample Size & Confidence Intervals. S uppose we want to estimate the mean weight of a population of turtles. We collect a random sample of turtles with the following information: Sample size n = 25; Sample mean weight x = 300; Sample standard deviation s = 18.5; Here is how to find calculate the 90% confidence interval for the true .
For explorative research, a small sample size may suffice. Moreover, generally, the more important a study is, the larger the sample size required in order to satisfy the . determined by dividing the available funds for data collection by the average data collection cost per element. . Quantitative research designs tend to require larger sample Numeric data: Quantitative research uses numerical data to describe and analyze the phenomena under study, such as statistical analysis, surveys, and experiments. Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves large sample sizes to ensure statistical significance and to generalize findings to a larger population. The sample size used for the main statistical analyses (i.e., EFA, CFA, Cronbach’s alpha, etc.) amongst the studies varied. The largest sample size used was N = 15,847, while the smallest was N = 20. Sample sizes most frequently fell between the range of 100–300 participants (34%), followed by 301 to 500 participants (24%).
sample size in research example
Sample size is the number of observations or individuals included in a study or experiment. It is the number of individuals, items, or data points selected from a larger population to represent it statistically. The sample size is a crucial consideration in research because it directly impacts the reliability and extent to which you can generalize those findings to the . An important step when designing an empirical study is to justify the sample size that will be collected. The key aim of a sample size justification for such studies is to explain how the collected data is expected to provide valuable information given the inferential goals of the researcher. In this overview article six approaches are discussed to justify the sample size in .
What is Sample Size? ‘Sample size’ is a market research term used to define the number of individuals included in research. Researchers choose their sample based on demographics, such as age, gender, or physical location.The term can be vague or specific.. For example, you may want to know what people within the 18-25 age range think of your product. What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition, Uses & Methods. Published on June 12, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. The sample size for a study needs to be estimated at the time the study is proposed; too large a sample is unnecessary and unethical, and too small a sample is unscientific and also unethical. The necessary sample size can be calculated, using statistical software, based on certain assumptions. If n . Advances in this field help researchers more accurately predict the sample sizes needed for research designs that use qualitative data, to better forecast the time and cost of field research, and to justify sample sizes in grant proposals. . Potts H. W. (2015). Supporting thinking on sample sizes for thematic analyses: A quantitative tool .
sample size for small population
minimum sample size for survey
minimum sample size for research

web23 de nov. de 2017 · Curso de Raciocínio Lógico Matemático Quantitativo Abstrato Verbal - Exame Psicotécnico e teste psicológico de sequenciação numérica – Aula sobre como raciocinar logicamente com série de.
average sample size for quantitative research|100 respondents for quantitative research